The construction sector ranks second in raw material consumption, trailing only the food processing industry. Building materials are indispensable in construction, necessitating sustainable options for present and future generations. Consequently, there’s a growing interest in Alternative Building Materials to fulfill structural needs with lower energy and material consumption.
Increased global environmental consciousness and climate change concerns have spurred interest in eco-friendly building materials. Developing countries’ economic growth drives much of the global housing demand. Alternative building materials, such as modified conventional or indigenous materials, offer advantages like low embodied energy, ease of use, availability, and cost-effectiveness. These materials are suitable for various projects, including humanitarian engineering initiatives.
Sustainable options like straw bale, bamboo, and manufactured sand are gaining traction. Businesses, responding to regulations and client demands, are increasingly adopting responsible building materials to enhance corporate responsibility. Stakeholders across the supply chain, including clients, designers, contractors, and material suppliers, must prioritize sustainability.
Sustainable building materials offer a pathway for the construction industry to mitigate environmental impact and achieve sustainable development. Material selection is crucial in sustainable construction, ranking among the top five factors impacting sustainable development goals. Choosing sustainable materials is pivotal in minimizing environmental footprints.
Identification of Alternative Building Materials for Sustainable Construction Toward Sustainable Development
The housing challenges faced by individuals in Nigeria could see a significant reduction by employing Alternative Building Materials like durable laterite, which is culturally accepted, cost-effective, and poses no risk to human health. This approach could pave the way for achieving sustainable housing in terms of both quality and quantity.
Nigeria boasts various Alternative Building Materials such as adobe, bamboo, thatch, stones, timber, coconut trees, and grasses, among others. The abundant natural deposits of clay, laterite, stone, lime, agro-industrial waste, timber, bitumen, and glass sand in Nigeria complement the call for utilizing these local resources for construction purposes.
Pozzolanas represent innovative materials in the construction industry, characterized by siliceous and aluminous properties. While they may possess minimal cementitious value individually, when finely divided and in the presence of moisture, they chemically react with calcium hydroxide to form compounds with cementitious properties. Utilizing pozzolans brings about economic, environmental, and technical benefits, including improved concrete quality, enhanced workability, resistance to various types of deterioration, and increased water tightness. Examples of pozzolanas include Rice Husk Ash (RHA), Fly Ash (FA), Ground Husk Ash (GHA), Pulverised Burnt Clay (PBC), Saw Dust Ash (SDA), and Acha Husk Ash (AHA).
The combination of quarry dust and lateritic soil exhibits superior performance compared to mixtures like red earth and river sand+laterite+red earth (RLR) when employed as Alternative Building Materials for sandcrete block production. Many professionals in the construction industry concur that the use of Alternative Building Materials positively impacts the environment, particularly in terms of environmental protection.
However, researchers have identified several barriers hindering the widespread adoption of Alternative Building Materials, including lack of interest from clients, public perception issues, social acceptability concerns, doubts regarding durability and longevity, as well as the absence of standards and specifications. Despite their significant advantages, alternative building materials in Nigeria have not received adequate attention compared to conventional building materials.
Studies indicate that natural building materials are often viewed by experts as lacking in sophistication and performance. However, this skepticism among experts stems from a combination of factors, including a lack of understanding, limited practical experience, and cultural biases. The extraction and utilization of conventional construction materials contribute significantly to global warming due to the high energy requirements for their manufacturing processes. This highlights the necessity for global research efforts in construction materials development.
Such efforts are driven by various factors including the escalating costs of conventional materials, challenges in accessing financial resources for construction projects, the potential for recycling agricultural waste materials in construction, the biodegradability of materials, the imperative to maintain ecological equilibrium amidst population growth, and the persistent housing challenges.
Alternative Building Materials offer numerous advantages over conventional ones. They are comparatively affordable, promote cultural heritage, readily available, energy-efficient, reusable, and biodegradable. These attributes align with the fundamental principles of sustainable construction. Moreover, these materials are cost-effective when compared to imported alternatives, thus making them a viable option for construction projects within the country.
Evaluation of Classes (Types) of Alternative Building Materials for Sustainable Construction
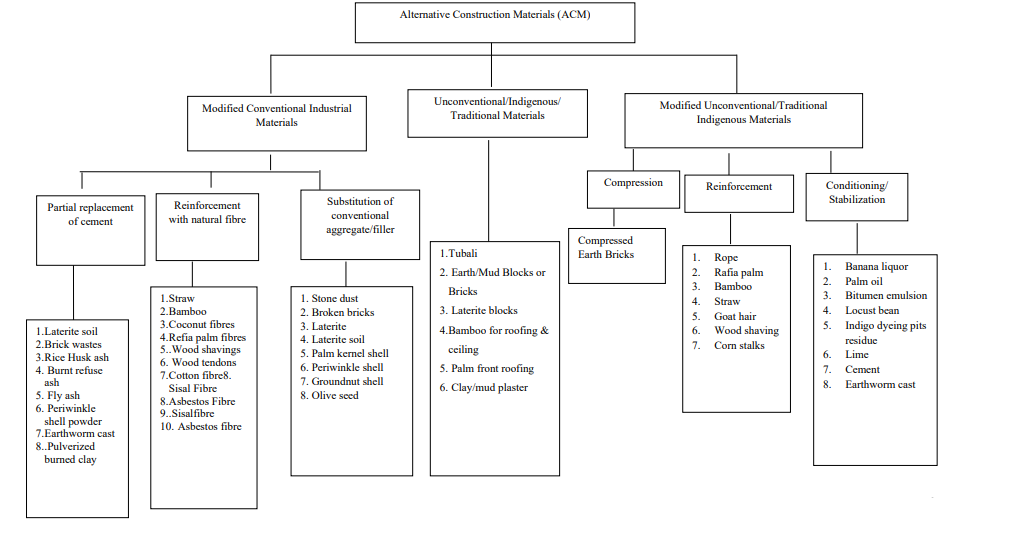
A comprehensive review of various studies on construction materials indicates that the development of Alternative Building Materials typically falls into one of three primary categories. Firstly, conventional materials may be altered with the primary aim of reducing their cost. Alternatively, modifications might be focused on enhancing unconventional materials, which belong to the category of alternative materials, with studies examining their properties for potential integration into contemporary construction practices. The main methods employed for altering original materials include partial replacement, substitution of constituents, compression, stabilization, and reinforcements.
While much of the research endeavors to reduce construction material costs, it often culminates in assessing the strength and a few other properties of the resulting materials, without thorough investigations into the economic implications of these innovations. These materials find applications in various aspects of construction, such as substructure/foundation, flooring, wall and structural frames, roofing, and finishes/fittings.
Notable Alternative Building Materials suitable for construction in Nigeria include Rice Husk Ash, Soil Bitumen Brick, and Micro Concrete Roofing Tiles. These materials align with previous findings based on engineering requirements, production and maintenance costs, transportation costs, availability, optimal production time, and durability.
Researchers have identified a range of Alternative Building Materials conducive to sustainable construction and development. These materials encompass a variety of natural resources such as laterite soil, brick wastes, rice husk ash, burnt refuse ash, fly ash, periwinkle shell powder, earthworm cast, pulverized burned clay, straw, bamboo, coconut fibers, wood shavings, cotton fiber, sisal fiber, stone dust, broken bricks, palm kernel shell, groundnut shell, olive seed, tubali, earth/mud blocks or bricks, palm front roofing, clay/mud plaster, compressed earth bricks, banana liquor, palm oil, bitumen emulsion, locust bean, indigo dyeing pits residue, lime, cement, and earthworm cast.
It is worth noting that some of these materials are still undergoing scientific testing regarding their mechanical properties. In summary, there are three main types of Alternative Building Materials: modified conventional industrial materials, unconventional/indigenous/traditional materials, and modified unconventional/traditional indigenous materials.
Features of Alternative Building Materials Towards Sustainable Development
The construction industry is responsible for shaping the built environment, establishing physical structures and infrastructure that dictate our levels of freedom and flexibility for decades to come. Sustainable development involves meeting human needs for natural resources, industrial products, energy, food, transportation, shelter, and waste management while safeguarding environmental quality and preserving natural resources for future generations.
Sustainable construction aims to minimize the environmental footprint of buildings over their lifespan while maximizing economic viability. This involves creating and managing a healthy built environment based on resource-efficient and ecological principles.
Research on sustainable construction materials is increasingly recognizing their environmental, social, and economic benefits. Sustainable materials are integral to sustainable development, particularly in addressing Nigeria’s significant housing deficit, largely attributed to the cost of conventional building materials. Two key features of sustainable building materials are their ecological and economic attributes. Ecologically, these materials should be recyclable, low in contamination, provide insulation and thermal conductivity, and be easily deconstructable. Economically, they should be readily available, affordable, flexible in use, and durable.
Sustainable building materials must also meet environmental standards, promoting environmental health by being free of toxic substances and emitting low levels of volatile organic compounds. Socially, these materials should have aesthetic and cultural value, as well as public acceptability. Functionally, they should demonstrate low energy consumption, excellent indoor air quality, robust technical performance, and durability.
The use of alternative building materials offers numerous benefits for sustainable construction. They contribute to waste reduction, pollution prevention, and embodied energy reduction during manufacture. In building operation, they enhance energy efficiency, promote conservation, and provide non-toxic, long-lasting, and waste management alternatives. Their utilization reduces transport costs, carbon emissions, and materials costs while also offering employment and skills development opportunities.
Sustainable building materials should be environmentally friendly, affordable, versatile, and long-lasting. For instance, timber has the capacity to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, unlike steel, concrete, and aluminum, which emit significant amounts of carbon dioxide. The environmental impacts of alternative materials like cob demonstrate significantly lower embodied energy and carbon compared to conventional materials, contributing to reduced global warming.
The adoption of sustainable building materials conserves resources, reduces environmental impacts, enhances environmental quality, and generates subsequent savings through improved productivity and waste reduction.
Conclusion
The utilization of Alternative Building Materials presents a promising avenue for addressing Nigeria’s housing deficits sustainably. Despite facing hurdles like skepticism and lack of standards, these materials offer economic benefits, environmental protection, and cultural preservation. Notably, pozzolanas and locally available resources show potential for sustainable construction. However, comprehensive research and overcoming barriers are essential for their widespread adoption.
Sustainable building materials must fulfill ecological, economic, social, and functional requirements, ensuring they contribute positively to construction practices while safeguarding the environment and meeting societal needs. Overall, embracing Alternative Building Materials is critical for achieving sustainable development in Nigeria’s construction sector.



