Flooding is a persistent and escalating challenge in Nigeria, characterized by the overflow or retention of water in areas that are typically dry. This inundation is detrimental to the inhabitants, affecting humans, plants, and animals. Flood hazards primarily impact buildings, lives, and properties housed within these structures, often leading to significant emotional, social, and economic costs.
Floods are defined and categorized based on their causes, types, and the extent of damage they inflict. Common types include pluvial flooding, groundwater flooding, tidal flooding, fluvial flooding, flooding from sewers, and flooding from man-made infrastructure. The vulnerability of Nigerian buildings to these floods is a significant factor in the high levels of disruption and damage experienced during such events.
The Importance of Resilience in Flood Risk Management
Resilience, the ability of a system to recover from disturbances, is crucial in mitigating the adverse effects of floods. A resilient environment can manage flood occurrences with minimal loss or damage and recover quickly.
Nigerian buildings and infrastructures, however, have shown a higher vulnerability to floods compared to global trends. This indicates a pressing need to enhance the resilience of Nigerian urban systems to cope with increasing flood risks.

Developing Resilient Buildings in Nigeria
Building resilient structures involves several practical steps and considerations, as highlighted below:
1. Identification of Flood-Prone Areas
Areas susceptible to flooding, such as those near rivers, swamps, and coastal regions, should be identified and documented. This information should be made available to state physical planning units, town planners, and prospective builders.
2. Determination of Flood Severity
The severity of potential flood events in identified flood-prone areas must be evaluated. Predictive models can help assess future flood risks, allowing for tailored flood management strategies.
3. Identification of Flood Causes
Understanding the sources and causes of floods in specific areas can aid in developing preventative measures. This knowledge prepares individuals and communities for potential dangers, reducing the element of surprise during flood events.
4. Development of Flood Maps
Visual representations of flood-prone areas should be created for easy interpretation. These maps should be available at national, state, and local levels to guide urban planning and development.
5. Implementation of Building Policies
Building codes and policies must incorporate flood resilience features. Specific building types and designs should be mandated in flood-prone areas to minimize vulnerability.
6. Enforcement of Resilience Laws
Laws should be enacted to ensure compliance with flood resilience policies. This includes discouraging activities that increase flood vulnerability and promoting adherence to resilient building practices.
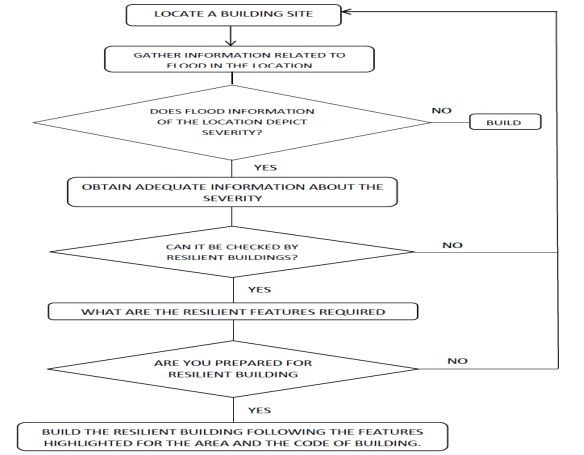
Expected Features in Resilient Nigerian Buildings
Achieving flood resilience in Nigerian buildings requires incorporating specific features, such as:
- Invulnerable Sites: Avoiding construction in flood-prone areas.
- Elevated Structures: Building storey buildings or structures with raised foundations to prevent floodwater entry.
- Tiled Floors and Walls: Using materials that resist water damage and facilitate quick recovery after flooding.
- Efficient Water Management Systems: Implementing rainwater harvesting and effective drainage systems to manage runoff.
- Proper Waste Disposal: Ensuring waste is disposed of in a manner that prevents blockage of drainage systems.
- Supportive Facilities: Equipping buildings with tools and materials like water pumps, life jackets, and flood warning systems to aid during flood events.
RELATED ARTICLE:
Bottom Line
The development of flood-resilient buildings in Nigeria is a multi-faceted approach that involves government policies, stakeholder involvement, and community participation.
Implementing comprehensive flood management strategies, incorporating resilient building designs, and ensuring strict adherence to resilience laws can significantly reduce the adverse impacts of floods.
While this endeavor requires substantial resources, the long-term benefits of reduced flood damage and enhanced community resilience far outweigh the costs. By learning from past disasters and adopting these proactive measures, Nigeria can build a future where its structures and communities are better prepared to withstand the challenges posed by flooding.



